A new ransomware family called ‘White Rabbit’ appeared in the wild recently, and as per the current researcher’s findings, could be a side-operation of the FIN8 hacking gang. FIN8 is a financially motivated attacker who has been addressed targeting financial organizations for some years, primarily by developing POS malware that can hijack credit card details.
What is the Simple Tool to Transmit Double-Extortion?
The first public mention of the White Rabbit Ransomware was in a tweet by a ransomware expert seeking a sample of the malware.
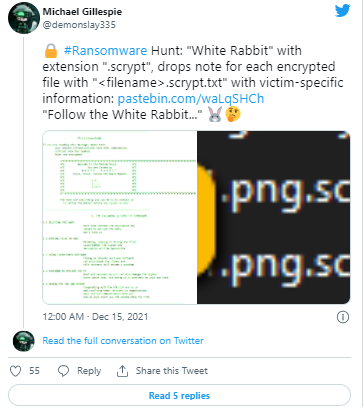
In the recent report, Investigators examine a piece of the White Rabbit ransomware obtained during an attack on a US bank in December 2021. The ransomware executable is a small payload, weighing in at 100 KB file, and requires a password to be entered on command line execution to decrypt the malicious payload.
A password to execute the malicious payload has been used previously by other ransomware operations, including Egregor, MegaCortex, and SamSam. Once executed with the correct password, the ransomware will scan all folders on the device and encrypt targeted files, creating ransom notes for each file it encrypts.
For example, a file named test.txt would be encrypted as test.txt.script, and a ransom note would be created named test.txt.scrypt.txt. While encrypting a device, removable and network drives are also targeted, with Windows system folders excluded from encryption to prevent rendering the operating system unusable.
The ransom note notifies the victim that their files had been eliminated and threatens to post and/or sell the seized information if the demands are not met.

The deadline for the victim to pay a ransom is set to four days, after which the actors threaten to send the stolen data to data protection authorities, leading to data breach GDPR penalties. The evidence of the stolen files is uploaded to services such as ‘paste.com’ and ‘file.io,’ while the victim is offered a live chat communication channel with the actors on a Tor negotiation site.
The Tor site includes a ‘Main page,’ used to display proof of stolen data, and a Chat section where the victim can communicate with the threat actors and negotiate a ransom demand, as shown below.
What are the Links to FIN8?
As noted in the Trend Micro report, evidence that connects FIN8 and ‘White Rabbit’ is found in the ransomware’s deployment stage. More specifically, the novel ransomware uses a never-before-seen version of Badhatch (aka “Sardonic”), a backdoor associated with FIN8. Typically, these actors keep their custom backdoors to themselves and continue to develop them privately. This finding is also confirmed by a different report on the same ransomware family undertaken by Lodestone researchers.
They too found Badhatch in ‘White Rabbit’ attacks, while they also noticed PowerShell artifacts similar to FIN8-associated activity from last summer. As the Lodestone report concludes: “Lodestone identified several TTPs suggesting that White Rabbit if operating independently of FIN8, has a close connection with the more conventional threat group or is mimicking them.”
For now, White Rabbit has limited itself to only targeting a few entities but is considered an emerging threat that could turn into a severe menace to companies in the future. At this point, it can be contained by taking standard anti-ransomware measures like the following:
- Deploy cross-layered detection and response solutions.
- Create an incident response playbook for attack prevention and recovery.
- Conduct ransomware attack simulations to determine gaps and assess implementation.
- Complete backups, test backups, confirm backups and preserve offline backups.