Various security investigators are compiling an easy-to-follow list of vulnerabilities ransomware groups and their affiliates are utilizing as initial access to hijack the victims’ network. All this was first initiated with a call to action that was initially made by a security incident response team, on Twitter over the weekend.
After then, with the help of some other contributors that joined his efforts, the list quickly expand to include security bugs found in the products from over a dozen of different software and hardware vendors.
While such flaws have been or still are abused by one ransomware group or another in past and recent attacks, the list has also been developed to include currently exploited bugs, as security researchers Pancak3 explained.
The list comes in the form of a diagram facilitating defenders with an initiating point for shielding their network framework from incoming ransomware attacks.
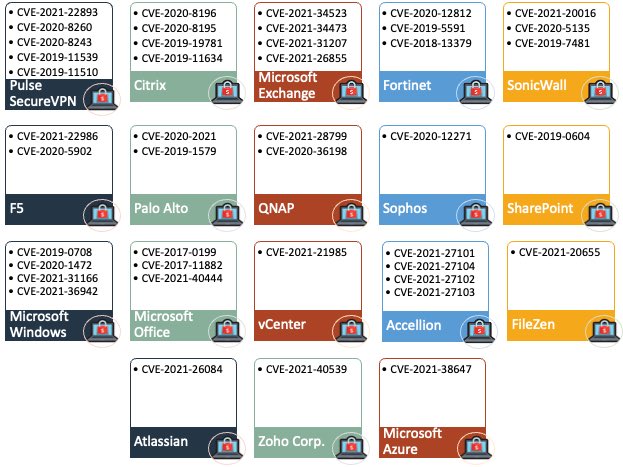
Vulnerabilities Addressed by Ransomware groups in 2021
In this year, ransomware groups and associates have attached many exploits to their arsenal, approaching currently abused vulnerabilities. For instance, this week, a revealed number of ransomware-as-a-service affiliates have initiated utilizing RCE exploits addressing the currently patched Windows MSHTML vulnerability (CVE-2021-40444).
At the starting of September, Conti ransomware also starts targeting Microsoft Exchange servers, hijacking enterprise networks using ProxyShell vulnerability exploits (CVEE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2021-31207).
In August, LockFile began extracting the PetitPotam NTLM relay attack method (CVE-2021-36942) to take over the Windows domain across the world, Magniber jumped on the PrintNightmare exploitation train (CVE-2021-34527), and eCh0raix was spotted targeting both QNAP and Synology NAS devices (CVE-2021-28799).
In July HelloKitty ransomware targeted vulnerable SonicWall devices (CVE-2019-7481), while REvil breached Kaseya’s network (CVE-2021-30116, CVE-2021-30119, and CVE-2021-30120) and hit roughly 60 MSPs using on-premise VSA servers and 1,500 downstream business customers.
FiveHands ransomware was busy exploiting the CVE-2021-20016 SonicWall vulnerability before being patched in late February 2021, as Mandiant reported in June. QNAP was also alert of AgeLocker ransomware attacks on NAS devices using an undisclosed bug in outdated firmware in April, just as an enormous Qlocker ransomware operation targeted QNAP devices unpatched against a hard-coded credentials vulnerability (CVE-2021-28799).
Again in the same month, Cring ransomware initiated encrypting unpatched Fortinet VPN devices (CVE-2018-13379) on industrial sector companies’ networks after a joint FBI and CISA alerting that the threat actors were scanning for vulnerable Fortinet types of equipment.
Microsoft Exchange servers worldwide were hit by the Black Kingdom and DearCry ransomware as part of a massive wave of attacks in March, directed at systems unpatched against ProxyLogon vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26858, CVE-2021-27065).
Here come another Clop ransomware attack against Accellion servers (CVE-2021-27101, CVE-2021-27102, CVE-2021-27103, CVE-2021-27104) that took place between mid-December 2020 and continued in January 2021 drove up the average ransom price for the first three months of the year.
How to Conflict Against Increasing Ransomware Threats?
In the Last month, When CISA was joined by Google Cloud, Microsoft, AT&T, Amazon Web Services, Crowdstrike, FireEye Mandiant, Lumen, Palo Alto Networks, and Verizon as part of the Joint Cyber Defense Collaborative (JCDC) partnership focused on defending critical frameworks from ransomware and other cyber threats.
The federal agency also released a new ransomware self-assessment security audit tool in June designed to help at-risk organizations understand if they’re equipped to defend against and recover from ransomware attacks targeting information technology (IT), operational technology (OT), or industrial control system (ICS) assets.
CISA facilitates a Ransomware Response Checklist for organizations that have been hit by a ransomware attack, advice on how to protect against ransomware, and answers to frequently asked questions about ransomware. The New Zealand Computer Emergency Response Team (Cert NZ) has also recently published a guide on ransomware protection for businesses.
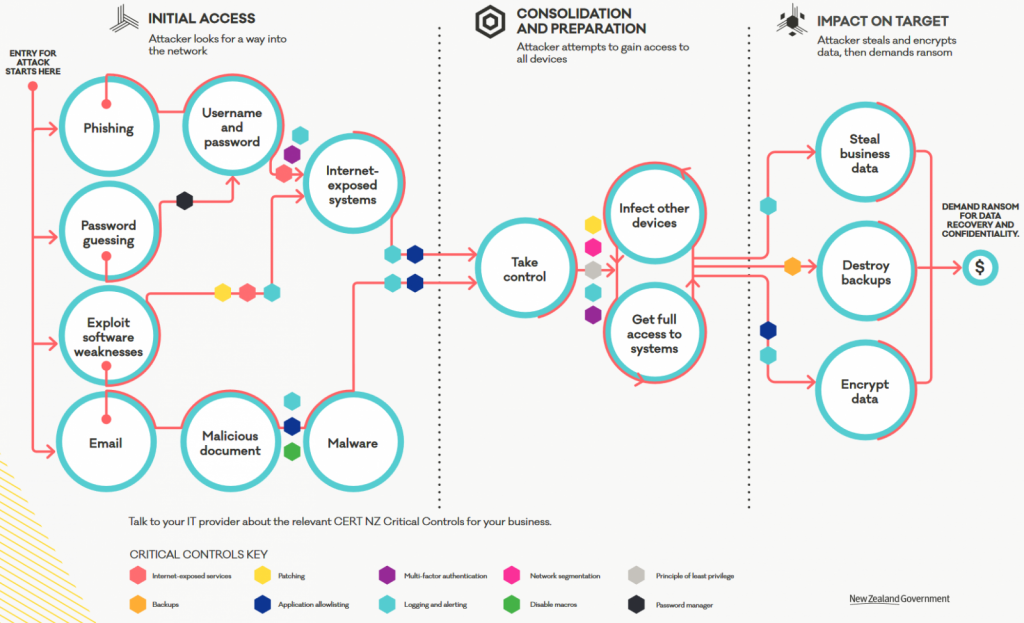
CERT NZ’s guide outlines ransomware attack pathways and illustrates what security controls can be set up to protect from or stop an attack.