A well-known Python-based machine learning and artificial intelligence project known as TensorFlow, developed by Google has discontinued the support for YAML, to patch the sensitive code execution vulnerability.
Yet Another Markup Language or YAML is a beneficial choice among developers seeking a human-readable information serialization language for managing configuration files and data in transit.
What is the Unauthorized deserialization Vulnerability in TensorFlow?
Handlers behind both the TensorFlow and Keras, a wrapper operation for TensorFlow, have patched an unauthorized deserialization vulnerability that derives from unsafe parsing of YAML. Tracked as CVE-2021-37678, the critical bug that allows the threat actor to run arbitrary code when an application deserializes a Keras model provided in the YAML format.
These Deserialization vulnerabilities typically occur when an application reads malformed or malicious information originating from unauthentic sources. After an application goes through and deserializes the information, it may smash resulting in a Denial of Service (DoS) condition, or worse, run the threat actor’s arbitrary code.
This YAML deserialization vulnerability rated a 9.3 in severity, was responsibly reported to TensorFlow handlers by a security researcher. But what are the sources of the flaw? The well-known “yaml.unsafe_load()” function in TensorFlow code:
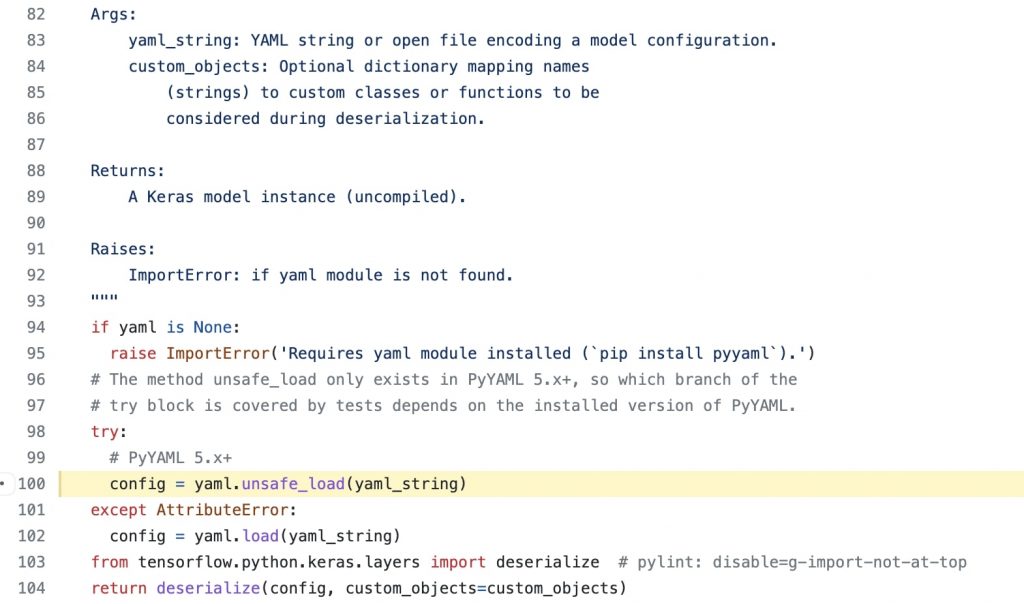
The “unsafe_load” function is known to deserialize YAML data rather liberally—it resolves all tags, “even those known to be unprotected on unauthenticated input.”
This means, admirably “unsafe_load” should only be called on input that comes from a trusted source and is known to be free of any malicious content. Should that not be the case, the threat actor can exploit the deserialization tools to run code of their choice by inserting malicious payload in the YAML data which is yet to be serialized.
An example of Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit transmitted in the vulnerability advisory demonstrated as given below:
from tensorflow.keras import models
payload = ”’
!!python/object/new:type
args: [‘z’, !!python/tuple [], {‘extend’: !!python/name:exec }]
listitems: “__import__(‘os’).system(‘cat /etc/passwd’)”
”’
models.model_from_yaml(payload)
TensorFlow drops YAML altogether in Assistance of JSON
Right after the vulnerability was reported, TensorFlow was determined to drop YAML support altogether and utilize the JSON deserialization instead. “Provided that the YAML format support requires a significant amount of work, we have removed it for now,” stated the project handlers in the same advisory.
“The ways ‘Model.to_yaml()’ and ‘keras.models.model_from_yaml’ have been replaced to raise a ‘RuntimeError’ as
They can be harmed to cause arbitrary code execution,” also explain the release notes associated with the fix. “It is suggested to use JSON serialization instead of YAML, or, a better alternative, serialize to H5.”
TensorFlow is not the first or only operation found to be utilizing YAML’s unsafe_load. The process’s use is rather avoided in Python projects. GitHub shows thousands of search results ascribing the function, with some of the developers come up with the improvements:
Fix for CVE-2021-37678 is expected to come in TensorFlow version 2.6.0, and will also be backported into the previous versions 2.5.1, 2.3.4, state the handlers.



